Typology and development
Original text in Ukrainian here >>>
This article is about how each of Jung’s 8 personality types manifests in social life.
Part 1 - Social Roles
Part 2 - Neurotic Roles and Manipulations
 Part 1
Part 1
The Social Roles
The social role is a kind of social portrait of a psychologically mature person of a certain type, who constructively uses his qualities both for his own social adaptation and for the common good. Each of the 8 types is characterized by innate predispositions to a particular activity. A person's strengths resonate with the corresponding demand from society – this is the main condition for the successful realization of a person's vocation and for feeling happy in his or her place.
Each of the eight social roles is a natural consequence of the manifestation of one of eight Jungian psychological functions.
A person's increasing maturation or increasing stress have a significant influence on how the person is expressing his or her type. If a person has a lot of internal conflicts, then a huge part of his or her efforts and energy is spent on these conflicts, so he does not have the strength to realize his potential for good of society and to fulfill a social role. Such a person’s social role is distorted by manipulation and various destructive neurotic games. Each type has his own manipulations.
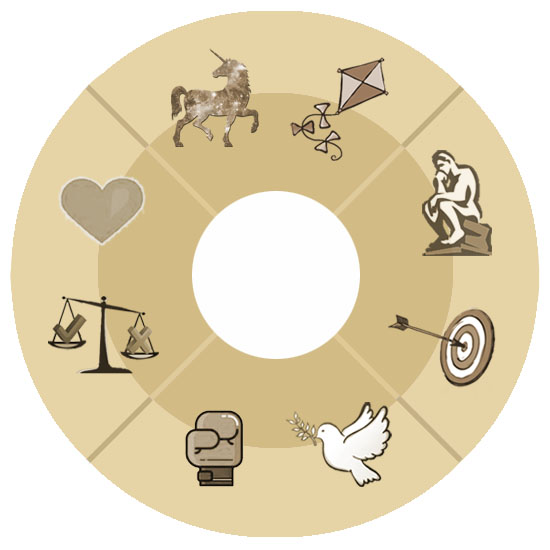
EIGHT MAIN SOCIAL ROLES
● Decisive PATRON – takes responsibility for others, believes that he should be a patron, a support for others: provides them with financial and material resources, protects them from the dangers of the outside world.
The role of Patron is activated in situations of physical threat, conflict, physical confrontation. Patron strongly defends his/her people, rushes headlong towards the adversary, stands up for the weak and defenseless, demonstrates physical strength and bravery. He takes indecisive and fearful people under his protection, helping them to act in the physical world, supporting them financially. Satisfied when he receives for this fidelity, subordination of others and recognition of his power and influence.
Under the mask of a strong person, he hides his weakness, sensitivity and dependence on others.
* * *
● Peaceful CAREGIVER – monitors the satisfaction of the physical and everyday needs of others, strives to feed, warm and create comfortable living conditions for everyone, tries to reconcile everyone. ☔️
The role of Caregiver is activated in situations of physical discomfort: cold, hunger, tension, disease, fatigue. He will always feed the hungry, warm the frozen, organize a cozy place to rest for a tired person, provide the sick with the necessary care, help a tense person relax. He is inclined to take care of creatures who can't manage unaided their everyday matters and unable to meet their physical needs. Satisfied when he receives for this a peaceful connection of others with himself (without conflicts, without pressure on him and without restricting his freedom of action), entertainment, novelty and recognition of his ability to create physical comfort.
Under the mask of a calm and friendly person hides anger, tension and internal discomfort.
* * *
● Sociable ALTRUIST – provides emotional support to others, reacts to being addressed, interested in the problems of others, always ready to cheer up and help.
The role of Altruist is activated when interacting with people who do not know how to engage in emotional interaction with others and who have a low mood. Then he begins to play the role of a friend, assistant, personal life coach: he shows benevolence and interest in his interlocutor, tries to lift his spirits and help in solving problems, involves him in social interaction. Satisfied when he receives for this gratitude, admiration and recognition that he is needed and occupies a special place in the life of others.
Under the mask of a helper, he hides his indifference and the need to receive attention from others.
* * *
● Responsible EDUCATOR – takes responsibility for maintaining correct behavior and for moral self-improvement. He tries to correct any flaw in himself and become a moral authority for others.
The role of Educator is activated when interacting with ill-mannered, irresponsible, dishonest people who deceive, steal and have unworthy desires. By his behavior, the Educator shows them an example of responsibility and honesty, helps them to understand moral issues, talks about the rules of communication in the community. Satisfied when he receives for this respect from others, following his instructions and recognition of his moral authority.
Under the mask of a righteous individual, he conceals “unworthy” thoughts and “dirty” desires.
* * *
● Efficient HERO – sets goals and develops algorithms of actions for their achievement in the shortest time, organizes processes that ensure the desired result. He tries to solve quickly any problem, constantly improves his skills.
The role of Hero is activated in situations requiring a fast intellectual reaction and achievement of a visible practical results. The Hero enthusiastically takes action to solve the issue, if he or she is sure that he will cope with it quickly and come out of the situation as a hero, while demonstrating his or her intelligence and gumption. When interacting with responsible, hardworking but low performing people, the Hero helps them properly allocate resources, provides step-by-step instructions to achieve the set goals. Satisfied when he receives for this admiration for his outstanding abilities, high appreciation of professionalism and recognition of his value to others.
Under the mask of a "successful success" he hides his failures, setbacks and fear of losing image.
* * *
● Competent THINKER – wants to find answers to all questions and to play the role of a teacher giving knowledge to others. He dives deep into the study of the issue, organizes and classifies information.
The role of Thinker is activated when interacting with emotional people who are not inclined to analyze information and to formulate logical conclusions. He or she thoroughly analyzes the data, searching the causes and helps others to make sense of the complex issues. Reveals logical inconsistencies, disturbance of structure, tries to be objective and impartial. Has a strong sense of justice and order, which he or she transmits to those around him or her. Satisfied when others show interest in his concepts and conclusions, need his explanations, listen attentively and recognize that his understanding of the world is the most correct.
Under the mask of an intellectual expert, he hides his insecurity and insolvency in other life areas.
* * *
●Optimistic INVENTOR – sees the diversity of opportunities and people's potential, gives others confidence in their abilities, shows creativity in solving problems, and inspires others with his optimistic vision.
The role of Inventor is activated when interacting with ordinary down-to-earth people living a monotonous life, not seeing their potential and not believing in their capabilities. Inventor encourages them to search for something new and unknown, broadens their outlook, reveals hidden talents, finds new ways to solving their problems, helps realize their potential. Satisfied when others admire his innovation, carelessness and vision of opportunities.
Under the mask of an initiative optimist, he hides boredom, fear of facing pain and restrictions.
* * *
● Devoted FORECASTER – thanks to a developed intuition, he or she is good at assessing prospects of projects and suggests the best time for action. Takes an individual approach to each person, tunes in to him or her. ✨
The role of Forecaster is activated when interacting with active, insensitive materialists who are not aware of either their inner states or the states of those around them, who act first, then think. Forecaster is showing his loyalty to such a person, acts in his/her interests, resonates with his/her deep world, reflects it, helps to realize the unmanifested, hidden, foresees consequences of planned actions and warns of possible danger. When interacting with a group of people (collective), he proves his devotion to it, tunes in to the deep collective state, maintains the unity of the group, inspires the realization of a common idea. Satisfied when others consult with him and act according to his forecasts, protect and support him financially, recognize his subtle perception.
Under the mask of a loyal follower, he hides aggression, rebelliousness and a desire to betray.
* * *
Usually an individual has several social roles, which he or she manifests depending on the situation.
* * * * *
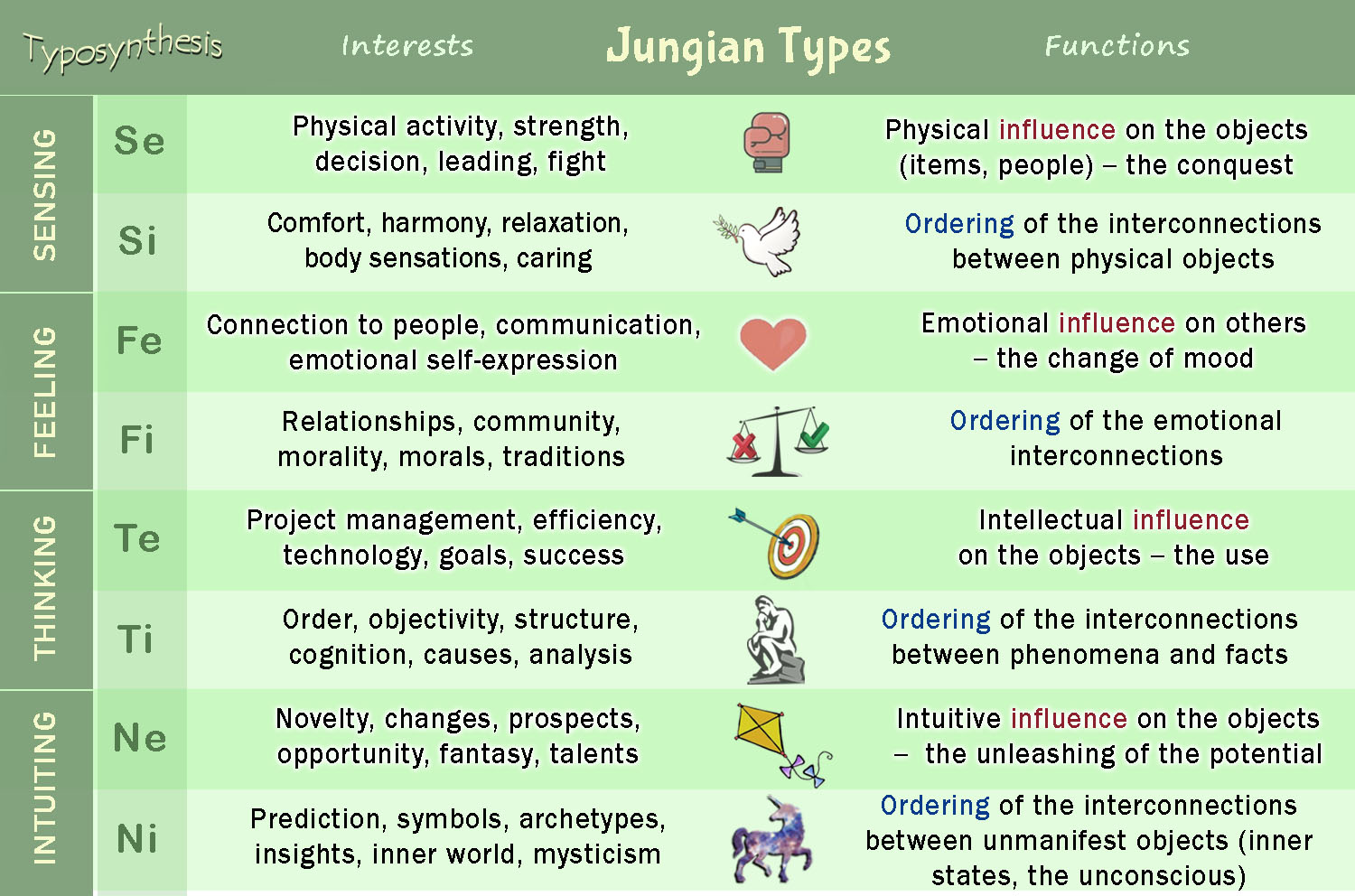
Carl Jung discovered four basic psychological functions: sensation, feeling, thinking and intuition. Dr. Jung found that each of these four psychological functions can have an introverted or extraverted orientation, depending on where a person's attention is directed: to external objects or to internal interconnections between objects. Thus, eight functions or eight types are obtained.
Sensing Extraverted (Se) – physical influence on the objects (items, people) – the conquest
Sensing Introverted (Si) – Ordering of the interconnections between physical objects
Feeling Extraverted (Fe) – Emotional influence on others – the change of mood
Feeling Introverted (Fi) - Ordering of the emotional interconnections
Thinking Extraverted (Te) – Intellectual influence on the objects – the use
Thinking Introverted (Ti) - Ordering of the interconnections between phenomena and facts
Intuiting Extraverted (Ne) – Intuitive influence on the objects – the unleashing of the potential
Intuiting Introverted (Ni) - Ordering of the interconnections between unmanifest objects (inner states, images of unconscious, archetypes)
* * * * *
2.1. Dependence on "self-image".
2.2. Manipulation and self-esteem.
2.3. Psychological dynamics of type
Dr Jung stressed the importance of studying typology for understanding the nature of neurosis:
«The qualities of the main conscious function, i.e., of the conscious attitude as a whole, are in strict contrast to those of the unconscious attitude… The conscious attitude is always in the nature of a worldview, if it is not explicitly a religion. It is this that makes the type problem so important. The opposition between the types is not merely an external conflict between men, it is the source of endless inner conflicts; the cause not only of external disputes and dislikes, but of nervous ills and psychic suffering.» (1)
Let's look at why the main conscious function is essentially a worldview and how typological features are related to internal conflicts.
The human personality is formed at the junction of external influences of society on man and internal innate qualities that man expresses to the world. Each of the 8 psychological types of people has their innate tendencies and develops the appropriate qualities and knowledge-abilities-skills, which allows him/her to express himself/herself in the world as well as possible, adapt in society and fulfill his or her social role, taking into account the demands of society.
Consider on example of two types (Se and Ni), how the main psychological function is manifested in human behavior in social life.
The function SENSING Extraverted (Se) helps a person perceive the objects of the physical (material) world and act confidently in it. The function INTUITION Introverted (Ni) helps a person to perceive and order the intuitive world (the world of intangible, unmanifested objects).
● Type with the main function SENSING Extraverted (type Se) focuses on physical reality, is well versed in the world of material objects, is practical and pragmatic, characterized by high physical activity, physical strength, independence, confident advancement in the physical world, decisive overcoming of obstacles, inclination to confront and to lead others. Due to these innate qualities, type Se in social life can exhibit the social role of a Decisive PATRON.
● Type with the main function INTUITION Introverted (type Ni) focuses on the non-material side of life, is well versed in the unmanifested world of ideas, symbols, inner meaning of objects, feels the passage of time well, is distinguished by insight and sensitivity, feeling of the deep world of other people, intuitive premonition of development of events and the ability to purposefully use one's own imagination. Due to these innate qualities, type Ni in social life can exhibit a social role of Devoted FORECASTER.
2.1. Dependence on "SELF-IMAGE".
By fulfilling his or her social role, a person gets the feeling of realization from the natural expression of the qualities of his or her type. In the process of self-expression, a person evaluates his or her qualities by himself/herself, as well as takes into account the evaluation of others. When combining these two assessments (external and internal), a person's idea of himself/herself, or "SELF-IMAGE" is formed. Over time, many people become identified with this "self-image", i.e., a person starts to think that he or she is a certain set of qualities and micro-roles, and that he or she does not exist without them. Then there is a need to maintain this image both in his/her own eyes and in the eyes of others, as well as the need to constantly improve his or her skills and create a "better version of himself/herself."
Each type, having identified with his or her most pronounced traits and qualities, becomes hostage to one’s " SELF-IMAGE": Qualities that are impersonally expressed by a person in the world -->> qualities that are expressed in the world through me -->> I possess these qualities -->> I am a set of different qualities and without them I am gone.
● Type Se starts to believe that his or her innate qualities: strength, confidence and ability to influence the situation and other people - this is who he or she is, i.e., he or she begins to think about himself/herself: "I am confident, strong, influential, independent."
● Type Ni starts to believe that his or her innate qualities: insight, intuitive premonition of development of events, feeling of the deep world of other people - this is who he or she is, i.e., he or she begins to think about himself/herself: "I am insightful, sensitive, I am one who feels the deep world of others ».
SELF-IMAGES OF DIFFERETNTS TYPES:
* I am confident, strong, influential, independent
* I am harmonious, peaceful, dwell within unity with others
* I am loving, good, needed by others ❤️
* I am correct, moral, I am improving
* I am successful and efficient, valuable to society
* I know and understand everything, I can explain everything
* I am resourceful, optimistic, discovering new things
* I am insightful, sensitive, I feel the deep world of others ✨
Which image is closest to you?
When a person is identified with the "self-image", the social role becomes NEUROTIC. A person makes continuous efforts to maintain a certain "self-image" both for oneself and for others, he or she tries to create a "better version of oneself" through self-improvement, the formation of new, better, more qualitative knowledge, skills and abilities.
"Self-image" or "psychological double" is constantly self-reproducing in every socially significant situation. If a person manages to maintain his "self-image", then he or she has high self-esteem, if he or she fails, then his or her self-esteem drops.
● Type Se, in order to confirm his or her "self-image" (I am strong, influential, independent), needs others to obey him or her, show unconditional loyalty to him or her, recognize his or her influence and power.
●Type Ni, in order to confirm his or her "self-image" (I am insightful, sensitive, I feel the deep world of others), needs others to consult with him and act according to his forecasts, to protect him or her from the gross physical world, to support him materially, to recognize his or her subtle perception.
The social need for recognition by others the qualities that are significant for the person oneself (one’s "self-image"), is one of the strongest motivations to engage into a "giving in order to get" exchange with others. However, the expression "giving in order to get" does not imply equal mutual assistance “You give me, I give you”, a favor for a favor, but a disproportionate exchange: “I give you social assistance, and you support my self-esteem for this.”
"Psychological double" (or "self-image") brings psychological tension, because being an artificial, collateral entity, it constantly fights for the impossible - for others to recognize it as genuine, authentic, real. This hopeless struggle for the confirmation of "self-image" draws (drains) much energy on itself and is accompanied by physical and mental exhaustion. The greater the difference between a real person and an imagined "self-image", the greater the person's neurosis. (2)
●Type Se, in order to confirm his or her "self-image" (I am strong, influential, independent), takes responsibility for others in the material, physical world, tries to be a support for others: provides them with material resources and protection from dangers, enhances their self-confidence. Takes the initiative in his own hands, solves for others their problems in the physical world.
To provide for others, he or she works hard, neglecting personal needs and rest. Wears a mask of a strong, steadfast person who firmly "takes a punch" and confidently overcomes obstacles. Demonstrates to others that he or she can handle everything on one’s own. "I am the one on whom everything depends, I'm in charge of everything." Avoids any manifestation of his or her weakness in public. Takes on more responsibility than one’s health allows. Drives himself/herself to complete physical exhaustion.
If it happens that after receiving help from Se type (protection and material support), a person gratefully leaves to get on with one’s life, the Se type can be really disappointed and feel the pain of betrayal. After all, he expected that the person, in response to his or her actions would support one’s self-esteem: to obey him or her and show unconditional loyalty.
●Type Ni, in order to confirm his or her "self-image" (I am insightful, sensitive, I feel the deep world of others), takes responsibility for others in the subtle, intuitive, deep world: takes an individual approach to each person, tunes in to him or her, enters into resonance with his or her deep world, helps to realize the unmanifested, hidden, warns of possible danger, predicts the development of events.
Wears a mask of a special, insightful, sensitive person, not like others, who feels everything more deeply than others, feels a deep unity with others. He or she adjusts to the mood of others, demonstrates loyalty to others, puts one's own interests aside, shows great self-giving. By his/her actions, proves that others can always rely on him or her. Relationships become a huge burden for him or her because of the sense of duty he or she imposes on himself/herself.
If it happens that after receiving help from Ni type (devotion and psychological support), a person gratefully leaves to get on with one’s life, the Ni type can be really disappointed and feel the pain of abandonment. After all, he expected that the person, in response to his or her actions would support one’s self-esteem: to consult with him or her and protect from the gross physical world.
The neurotic role is always like running in a circle, in which a person drives himself/herself, and then does not know how to get out of it. At the same time, the person, having identified with one’s fragment (e.g., with qualities of one’s main function), loses sense of integrity.
2.2. Manipulation and self-esteem.
Neurotic role is only one of the forms of manifestation of a person's dependence on "SELF-IMAGE". As this dependence increases, the neurotic role can turn into more gross and disharmonious manifestations, such as manipulation.
What is manipulation and why people manipulate others?
Here is the definition of manipulation from the American Psychological Association’s Dictionary of Psychology : “Manipulation or emotional manipulation is the use of means to exploit, control, or otherwise influence others to one’s advantage”.
In other words, manipulation is an indirect way of influencing others in order to change their perception or behavior to one’s advantage.
In the context of typology, the manipulator's advantage is in supporting one’s self-esteem.
Therefore, the definition of manipulation from a typological perspective can be as follows:
MANIPULATION is an indirect way of influencing others to get the desired reaction or behavior from them in order for others to support one’s SELF-ESTEEM.
Manipulator requires others to interact with him/her only in ways that support one’s self-image.
● Manipulation of the type Se – DOMINANCE.
In order to confirm one’s "self-image" (I am strong, influential, independent), type Se exaggerates one’s strength and influence, shows the "Alpha male" syndrome - makes it clear to others that he or she is the boss around here. Demonstrates one’s power and status, puts pressure on others, intimidates, threatens, humiliates, shouts in order to oppress the will of others. Keeps others in tension, demands that they do as he or she wants, goes into open confrontation, announces senseless orders and prohibitions. Becomes jealous and vindictive, can "strangle" his or her partner with control. Unable to control one’s bursts of anger. May resort to the use of physical force.
● Manipulation of the type Ni – VICTIMHOOD.
In order to confirm one’s "self-image" (I am insightful, sensitive, I feel the deep world of others), type Ni demonstrates one’s hypersensitivity, anxiety, scare, suffering and impotence, exaggerates the threats of the physical world, believes that he or she cannot cope with them, and others are not doing enough to help him or her. Takes offense and provokes in order to force others to act in one’s interests, supply him or her with resources and protect from threats. Plays the role of "victim" to impose the role of "savior" on another. Believes that the stronger his/her suffering, the more he or she deserves special treatment. Frustrated when others do not take responsibility for his life, do not solve his problems and do not reduce his anxiety and emotional pain.
Manipulations of different personality types:
* DOMINANCE - Wants to have power over others. Demonstration of one's strength and status, pressure on others, threats, intimidation, humiliation, bullying, psychological and physical violence.
* SABOTAGE - Wants to look peaceful, therefore outwardly demonstrates agreement with others, while inwardly resisting: doing something very slowly, 'forgetting' about his/her promises, remaining silent.
* DEMONSTRATIVENESS - Strong need to draw attention to oneself by imposing the role of spectators / listeners on others. Emotional pressure, mood swings, hysteria that passes as soon as the audience disappears.
* CONDEMNATION - Wants to be "correct". Corrects others, censures, imposes a sense of guilt. Flexibly regulates the psychological distance: repels the "wrong" ones and brings closer those who have "reformed".
* DECEPTION - In order to appear successful, creates a false attractive image and tarnishes others, falsifies the facts. Uses others, deceives to appropriate their resources.
* DETACHMENT - Wants to be competent, to know and understand everything, to explain and teach others. Selective communication only with those who share his picture of the world and only on topics in which he is competent. Detachment from all others.
* INFANTILISM - Thanks to one’s developed imagination, directs the potential and resources of people to the implementation of one’s own ideas and projects, encourages others to do uninteresting, hard work instead of oneself. Requires that others provide for him or her a life of comfort, entertainment and ease, avoids boredom and routine.
* VICTIMHOOD - Demonstrates one’s hypersensitivity and scare, takes offense and provokes in order to force others to act in his interests, supply him or her with resources and protect him or her from threats. Plays the role of "victim" to impose the role of "savior" on another.

Have you ever manipulated others?
❗️ Manipulation is a game that requires two players. You enter into a game with a manipulator in which you play the role he imposes on you: dictator - loyal subject, accuser - guilty, victim - savior, actor - spectator, omniscient - ignorant, infantile - guardian, etc. In relationships of this kind, one person’s neurosis dovetails with the other person’s neurosis. If one of the participants of interaction does not support manipulation, then it will not happen.
2.3. Psychological dynamics of type: two-way movement between harmony and disharmony
We have considered three gradations of type harmony: social role, neurotic role and manipulation.
* Social role - a person seeks to benefit society, he or she constructively and creatively shows his strengths, experiencing an inner desire to realize oneself, without expecting from others gratitude or help in return. A person feels one’s deep needs and does not depend on one’s "self-image", it is easy for him or her to be just oneself, he can afford not to manifest a social role if there is no motivation or energy at the moment.
* Neurotic role - outwardly it may not differ from the social role. At this level, a person no longer fully experiences one’s deep needs, he or she partially identifies with one’s qualities, with one’s "self-image", begins to depend on this image, is afraid of not responding to it, and wants others to constantly help him or her maintain this image. This forces him to play a social role even when he does not want to, the person tries to be constantly useful to others so that they support one’s self-esteem.
* Manipulation - at this level the psychological disharmony is more pronounced, a person spends one’s life energy in order to force others to recognize and support one’s "self-image", one’s self-esteem. Deep human needs are replaced by fragmentary superficial needs, the fulfilment of which cannot bring a sense of inner fullness and happiness. Person’s methods become destructive and after a brief boost of self-esteem as a result of manipulating others, the pleasure passes quickly, and a person may feel even deeper inferiority.
The more individual is dependent on "SELF-IMAGE", the more he or she is unbalanced and the deeper one’s neurosis.
Let's see how the behavior pattern of Ni type differs with different gradations of psychological harmony of the type:
* Social role - Devoted FORECASTER: thanks to a developed intuition, he or she is good at assessing prospects of projects, warns of possible danger, takes an individual approach to each person, tunes in to him or her, enters into resonance with person’s deep world, helps to realize the unmanifested, hidden.
* Neurotic role – a person shows the same qualities, but he or she is identified with one’s qualities, one’s "self-image" and wants others to support one’s "self-image". He or she has little understanding of one’s deep needs, begins to live in the interests of others, tries to become indispensable to them so that they support one’s self-esteem. Demonstrates that he or she feels everything more deeply than others, feels a deep unity with others, takes responsibility for others in the subtle, deep world, follows others, adjusts to others, puts one's own interests aside, demonstrates devotion to others. This leads to severe exhaustion.
* Manipulation – VICTIMHOOD. A person tries to get support from others for one’s self-esteem, giving nothing in return. Feels self-pity. Demonstrates one’s hypersensitivity and fears, takes offense and provokes in order to force others to act in one’s interests, supply him or her with resources and protect from threats. Plays the role of "victim" to impose the role of "savior" on another.
Behavior of the same personality type at different levels is very different, one might get the impression that they are different types. By understanding what kind of "self-image" is inherent to each of eight types and knowing the characteristics of the different gradations of psychological harmony of type, we can better understand whether different behavior patterns belong to the same type or to different types.
In general, for each of the 8 types, the following gradations of human psychological harmony can be distinguished (from total harmony to strong disharmony, from purity to pollution):
* PUEST MANIFESTATION OF FUNCTION - manifestation of one of the 8 main archetypes integrally and without distortions due to the process of individuation.
* SOCIAL ROLE - a person's strengths resonate with the corresponding demand from society.
* NEUROTIC ROLE - a person wants to be useful to society with its strengths, and in return expects support for one’s self-esteem.
* MANIPULATION - Through manipulation, a person tries to shake out desirable behavior from people in order to support one’s self-esteem.
* AGGRESSIVE IMPOSITION - forcibly dragging others into one's destructive scenario.
* SELF-DESTRUCTIVE DISAPPOINTMENT - the loss of hope that someone will support his or her self-esteem. Disappearance of any goals and motivations.
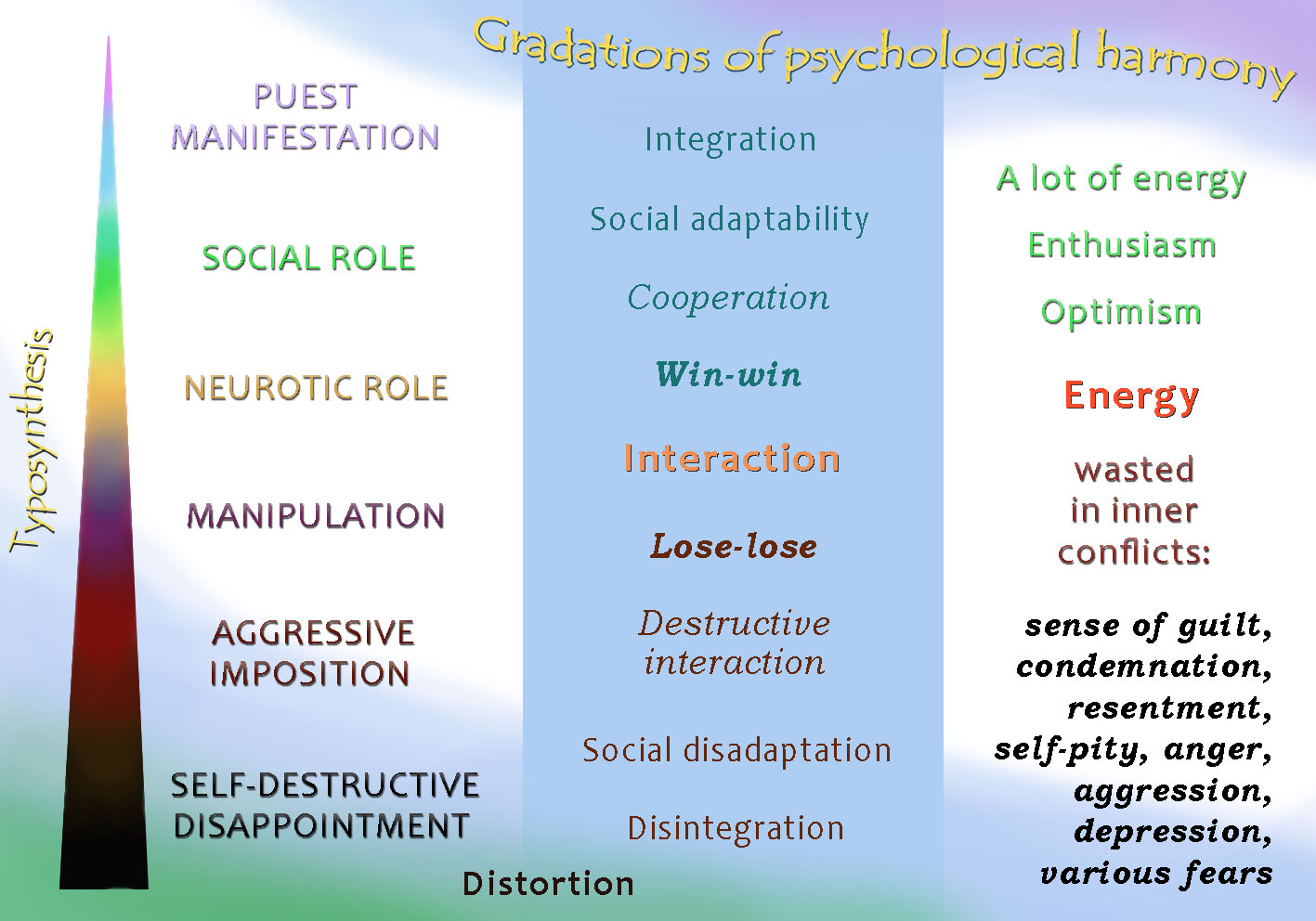
Thus, a person, knowing one’s type and knowing the degree of purity of the manifestation of one's type here and now, can better understand where he or she is and get an incentive to say farewell to manipulation and live according to one’s own inner nature. After all, everyone's deep aspiration is to be happy, and at the levels of disappointment, aggression, manipulation and neurotic role there is a lot of psychological tension and suffering.
* * *
1 - Source - Carl Jung "Psychological Types". A lecture delivered by Carl Jung at the International Congress of Education, Territet, Switzerland, 1923.
2 - While diagnosis “Neurosis” was removed from the "Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders" in 1980, the term is still often used informally to describe behaviors related to stress and anxiety.
* * *
Last updating 30.08.2022
